
If the vertical line touches the graph at more than one point, then the graph is not a function. If a vertical line is moved across the graph and, at any time, touches the graph at only one point, then the graph is a function. Use the vertical line test to determine whether or not a graph represents a function. Composite functions and Evaluating functions : f (2), g (3), fog (x), gof (x), fof (x), (f+g) (x) 3. For instance, in the function “2x = y,” y is dependent upon the value of x to determine its numerical worth. It handles variables like x and y, functions like f(x), and the modifications in the variables x and y. Measuring the rate of change of the function with regard to one variable is known as partial derivatives in mathematics. Evaluation of a function at the value of another (or the same ) is called composition of functions denoted as: f o g (x) f (g (x)) It is important to note that the composition of function is only defined if the range of the first is contained in the domain of second function. Composite Functions f(g(x)) f o g(x) 1) Start with inside function first. In math terms, the range (the y-value answers) of one function becomes the domain (the x-values) of the next function. If you compose the two functions and end up with. This partial derivatives calculator has the ability to differentiate a function numerous times. The term composition of functions (or composite function) refers to the combining of functions in a manner where the output from one function becomes the input for the next function. However, a function is an equation in which all of the variables are dependent upon the independent numbers in the mathematical statement. One use of function composition is for checking if two functions are inverses of each other. In the diagram below, function f has another function g as an input.

For example, f ( x ) − f ( y ) = x − y f(x)-f(y)=x-y f(x)−f(y)=x−y is a functional equation.įor example, in the equation “3 = x – 4,” x = 7. Each functional equation provides some information about a function or about multiple functions. The inside function is the input for the outside function. For instance, when they give you the formulas for two functions and tell you to find the sum, all theyre telling you to do is add the two formulas. Performing these operations on functions is no more complicated than the notation itself. f(g(x)) a function obtained by replacing x with g(x) in f(x). Now you will learn that you can also add, subtract, multiply, and divide functions. What is the Difference Between F of G of x and G of F of x 'f of g of x' is written as f(g(x)) and 'g of f of x' is written as g(f(x)).
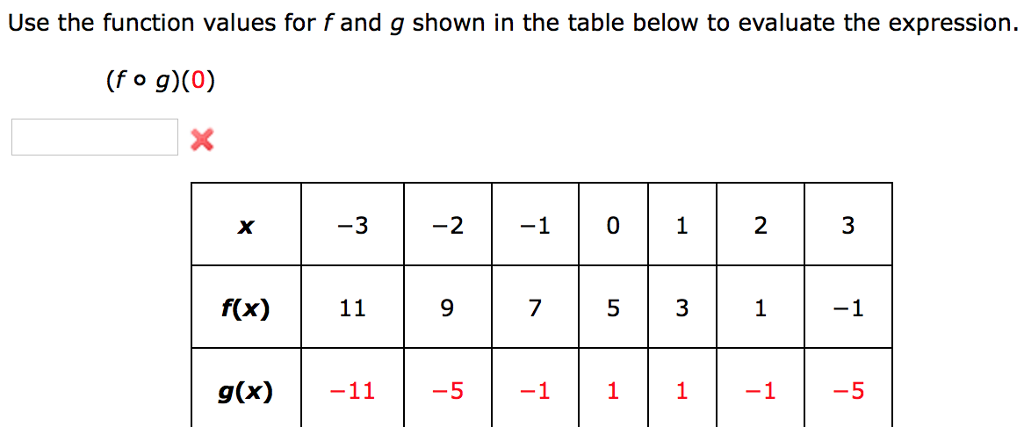
This last expression is read as “ y equals f of x” and means that y is a function of x.įunctional equations are equations where the unknowns are functions, rather than a traditional variable. Plug in the inside function wherever the variable shows up in the outside function. To find f(g(x)), we just substitute x g(x) in the function f(x). This function f(x) = 3x + 7 is read as the value of f at x or as f of x.Īn equation involving x and y, which is also a function, can be written in the form y = “some expression involving x” that is, y = f ( x).

To write such function in function notation, we simply replace the variable y with the phrase f(x) to get f(x) = 3x + 7. doi: 10.Later, Leonhard Euler formalized the usage of functions when he introduced the concept of function notation \(\color\)Ĭonsider a linear function y = 3x + 7. (1950), "Second-order transition temperatures and related properties of polystyrene", Journal of Applied Physics, 21 (6): 581–591, doi: 10.1063/1.1699711 In general, the accuracy of the Fox equation is very good and it is commonly also applied to predict the glass transition temperature in (miscible) polymer blends and statistical copolymers. Where w 1 and w 2 are weight fractions of components 1 and 2, respectively. In polymer chemistry and polymer physics, the FloryFox equation is a simple empirical formula that relates molecular weight to the glass transition. The Flory–Fox equation relates the number-average molecular weight, M n, to the glass transition temperature, T g, as shown below:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
